Heat Exchanger in HVAC Explained
- Aug 14, 2025
- 16 min read
Updated: Aug 18, 2025
Ever wonder what the real workhorse is behind your home's heating and cooling? It’s the heat exchanger in hvac systems, the unsung hero responsible for keeping you comfortable when the temperature drops. Simply put, this device moves heat from one place to another without the two sources ever actually mixing.
The Unseen Engine of Your Home's Comfort

The heat exchanger is an absolutely fundamental part of your furnace, yet most homeowners don't give it a second thought. Think of it like the radiator in your car. A car's radiator moves heat away from the engine to keep it from overheating. In the winter, the heat exchanger in your furnace does a similar job, just in reverse.
Here’s how it works. When your thermostat signals for heat, your furnace ignites its fuel, creating incredibly hot combustion gases. These potentially dangerous gases are completely sealed inside the heat exchanger’s metal walls, which are basically a network of tubes and chambers. As the metal heats up, your system's blower fan kicks on, pushing cool air from inside your house across the outside of these hot surfaces.
The heat naturally transfers from the metal to the air. This newly warmed air is then circulated through your ductwork to heat every room in your home. It’s a beautifully simple process that allows for an efficient transfer of warmth while keeping the air you breathe totally separate from harmful exhaust fumes, like carbon monoxide.
Why It Is So Important
The dual role of the heat exchanger, heating and protecting, is what makes it so vital. It’s not just about creating warmth; it's about doing it safely. This is precisely why checking the integrity of the heat exchanger is a top priority during any professional HVAC inspection. Even a tiny crack can have serious consequences.
A properly functioning heat exchanger is the barrier that stands between your family and potentially lethal combustion byproducts. Its role in maintaining both comfort and safety cannot be overstated.
This single component is central to your HVAC system’s performance. It influences everything from how cozy your house feels to how much you're paying in monthly energy bills. A clean, well-designed heat exchanger will operate at peak efficiency, meaning it squeezes more usable heat out of every bit of fuel it burns.
Getting to know this core component is the first step toward mastering your home’s climate control. It has a direct impact on:
Your Comfort: It’s directly responsible for creating the warm air that keeps you comfortable all winter long.
Your Safety: It provides the critical separation between the air you breathe and the toxic gases produced by burning fuel.
Your Budget: An efficient heat exchanger minimizes fuel waste, which leads to lower energy bills and significant savings over time.
Without a functional heat exchanger, your furnace would be little more than a fire in a box, completely unable to deliver warmth safely throughout your home. This foundational knowledge sets the stage for everything else: how the different types work, what to look for, and how to maintain them for safe, efficient operation for years to come.
How Your HVAC System Actually Exchanges Heat
To really get a handle on your home's comfort, you have to peek behind the curtain of your HVAC unit. It's not magic making your home toasty or cool; it’s just a clever use of basic physics, mainly conduction and convection. These two principles are the workhorses that move heat right where you want it.
At the heart of it all is the heat exchanger in hvac systems. Think of it as a thermal traffic cop, directing heat from one place to another without ever letting the two air streams, the air you breathe and the exhaust gases, actually touch. This separation is absolutely critical for keeping things efficient and, more importantly, safe.
The Heating Cycle: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
When you bump up the thermostat on a chilly day, you kick off a very precise chain of events inside your furnace. The end goal is simple: create heat and send it safely through your house. The heat exchanger is the undisputed star of this show.
Ignition and Combustion: First, your furnace ignites its fuel, which is usually natural gas. This creates incredibly hot combustion gases that are immediately sent into the sealed chambers of the heat exchanger.
Conduction, The Transfer Through Metal: These scorching gases heat the metal walls of the exchanger. This is conduction in action, just like how a metal spoon gets hot when you leave it in a fresh bowl of soup.
Convection, The Air Warms Up: At the same time, your system's blower fan kicks on. It pushes cool air from inside your home across the outside of those now-glowing metal walls. As the air moves over the hot surface, it picks up the heat. That's convection.
Circulation: This newly warmed air is then blown into your ductwork and distributed to every room, bringing the temperature up to your comfort level. Meanwhile, the nasty combustion gases, having done their job, are safely vented outside.
This all happens on its own, giving you steady warmth while keeping your indoor air clean. The condition of that heat exchanger is everything; it directly impacts how well and how safely this all works. To see how these critical parts hold up over time, check out our guide on the average lifespan of an HVAC system.
The Cooling Process: A Reversal of Roles
When summer hits, the whole process flips, but this time, your air conditioner’s evaporator coil takes center stage. It’s also a type of heat exchanger, but its mission is totally different.
Instead of creating heat, its job is to grab it and get it out of your house.
In cooling mode, the heat exchanger's job is not to generate warmth but to absorb it from your indoor air and transport it outside, leaving your home cool and comfortable.
Here’s how it pulls the heat right out of the air:
Absorbing Indoor Heat: Your indoor unit’s blower sucks warm, humid air from your living spaces across the ice-cold evaporator coil. This coil is filled with a special liquid refrigerant.
Refrigerant at Work: As the warm air passes over, the cold refrigerant inside the coil absorbs its heat. This heat absorption causes the liquid refrigerant to boil and turn into a gas. It’s the same principle that makes your skin feel cold as sweat evaporates.
Transporting Heat Outdoors: The refrigerant, now a warm gas, flows through copper lines to your outdoor condenser unit. There, another heat exchange happens. A big fan blows outdoor air over the condenser coils, releasing all that captured heat into the atmosphere.
Completing the Loop: As it sheds its heat, the refrigerant cools down and condenses back into a liquid. It’s then ready to cycle back inside and do it all over again.
This continuous loop is literally pumping the heat out of your home. Whether it's heating or cooling, the heat exchanger in hvac systems is the unsung hero making your home a year-round sanctuary.
A Guide to Different HVAC Heat Exchanger Types
When you hear the term "heat exchanger in hvac", it's easy to think of it as a single, one-size-fits-all part. But in reality, nothing could be further from the truth. The design of a heat exchanger is carefully picked based on the job it needs to do, the fuel source it's working with, and the efficiency goals of the system.
These differences are why you see such a wide variety of HVAC systems out there, from small furnaces in a home closet to massive units on a commercial roof. We'll walk through three of the most common designs you'll run into, breaking down how they're built, what they're good at, and where you'll typically find them.
This image really gets to the heart of how all heat exchangers work, showing the simple but powerful interaction between a hot fluid and a cold one.
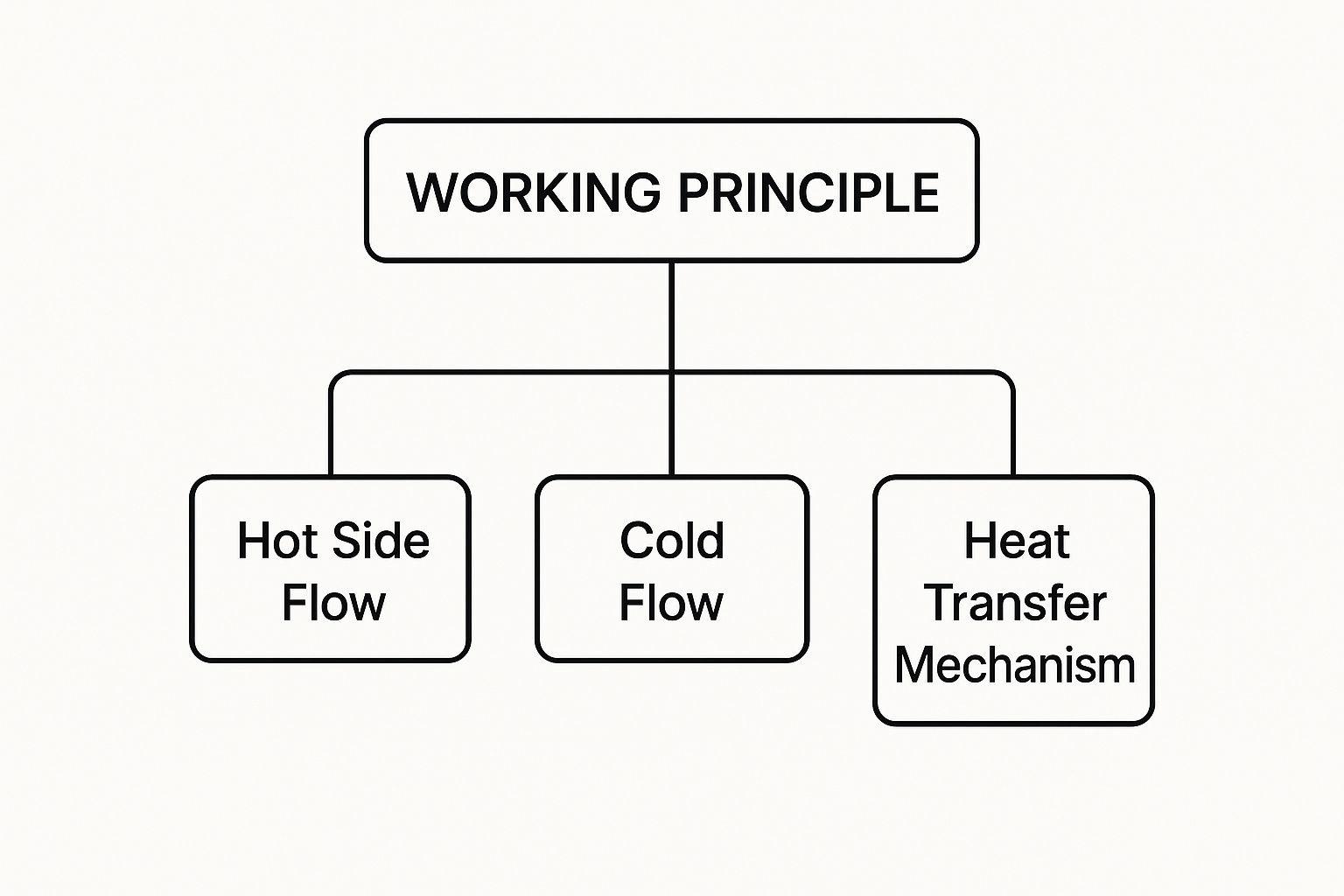
As the diagram shows, the whole process hinges on keeping two separate fluid streams moving through the device. This allows thermal energy to pass from one to the other without them ever mixing.
Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
First up is the workhorse of the commercial and industrial world: the shell and tube heat exchanger. It’s a classic, robust design. Just picture a large, tough cylindrical shell that’s packed with a bundle of smaller tubes running from end to end. One fluid, say, hot water from a boiler, flows through all the small tubes, while another fluid flows around the outside of those tubes, all contained within the shell.
The big win here is durability. This design can take a beating, easily handling high pressures and temperatures. Its straightforward, rugged build also makes it relatively easy to clean and maintain, which is a huge plus in demanding settings like large-scale building climate control.
Because they’re so big and heavy, you won’t find a shell and tube exchanger in your typical house. They’re much more at home in the boiler system of a large office building or a commercial water chiller, where their raw power and resilience are what matter most. If you want to know more about the systems you do find in homes, our guide to residential HVAC system types is a great place to start.
Plate and Frame Heat Exchangers
Next, we have the plate and frame heat exchanger, a true marvel of efficient, compact engineering. Instead of a big shell and tubes, this design uses a stack of thin, corrugated metal plates that are pressed tightly together inside a frame. These plates create a series of very narrow channels, with hot and cold fluids flowing through alternating passages.
The secret to its success is packing an enormous amount of surface area into a very small space. This incredibly dense design allows for heat to transfer between the fluids with astonishing speed and efficiency.
The genius of the plate and frame design lies in its surface area to volume ratio. It achieves a level of thermal transfer that would require a much larger shell and tube unit, making it perfect for space-constrained applications.
This combination of efficiency and a small footprint makes plate and frame heat exchangers incredibly versatile. You'll see them in everything from systems that provide domestic hot water to radiant floor heating setups and even some high-efficiency boilers. The only real trade-off is that those narrow channels can be more prone to clogging if the fluids aren't kept clean.
Microchannel Heat Exchangers
A newer player that’s quickly becoming a dominant force is the microchannel heat exchanger. These operate on a principle similar to your car’s radiator and are now the go-to choice for modern air conditioning condenser units. They're built from aluminum and use multiple flat tubes that contain dozens of tiny passages, or "microchannels," for the refrigerant to flow through.
The key advantages here are threefold: high efficiency, a compact size, and a reduced refrigerant charge. Microchannel coils are simply better at transferring heat than older fin-and-tube designs, which lets manufacturers build smaller, lighter, and more effective AC units.
The reduced need for refrigerant is a massive benefit, especially with the rising costs and environmental regulations around these chemicals. It's no surprise that microchannel technology is rapidly becoming the new standard for both residential and light commercial air conditioners.
Comparison of Common HVAC Heat Exchanger Types
To make sense of these options, it helps to see them side-by-side. Each design brings its own strengths to the table, making it the right choice for certain jobs.
Heat Exchanger Type | Design Principle | Primary Advantage | Common HVAC Application |
|---|---|---|---|
Shell and Tube | A bundle of tubes inside a large cylindrical shell. | Extreme durability and ease of maintenance. | Large commercial boilers and chillers. |
Plate and Frame | Corrugated plates stacked to form flow channels. | High efficiency in a compact size. | Domestic hot water, radiant heating. |
Microchannel | Flat aluminum tubes with very small internal channels. | Superior heat transfer with less refrigerant. | Modern air conditioning condenser units. |
Ultimately, every heat exchanger in hvac systems is a purpose-built component. By looking at how they're built and what they excel at, you can start to see why HVAC systems are designed the way they are; it's all about striking the right balance between performance, cost, and long-term durability to keep you comfortable.
How Heat Exchangers Impact Your Energy Bills
The performance of the heat exchanger in hvac systems is directly tied to your monthly energy bills. It’s a simple but powerful relationship. Think of it like the engine in your car: a finely tuned one gets the most mileage out of every gallon of gas. Similarly, a high-quality heat exchanger squeezes every last bit of warmth from the fuel it burns.
On the flip side, a dirty, damaged, or poorly designed one is a huge energy waster. It lets valuable heat escape right up the flue instead of sending it into your home. This means you're literally paying to heat the great outdoors, and that's a cost no one wants.
Understanding AFUE and Real-World Savings
So, how do you measure this efficiency? The key metric is the Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) rating. This number tells you exactly what percentage of the fuel your furnace consumes is converted into actual, usable heat for your home over a year. The heat exchanger's design and condition are the single biggest factors that determine this number.
For instance, a furnace with an 80% AFUE rating turns 80 cents of every fuel dollar into warmth. The other 20 cents? That's lost energy, vented outside as exhaust. Now, compare that to a modern, high-efficiency furnace with a 95% AFUE rating; it only loses 5 cents per dollar. You can see how that difference adds up over a long, cold winter.
A higher AFUE rating, driven largely by the heat exchanger, means more of your money becomes heat. This is the single most important factor in your furnace's long-term operating cost.
Let’s put some real numbers to it. Imagine you're upgrading from an old furnace with a 70% AFUE to a new 95% AFUE model. For every $1,000 you used to spend on heating fuel, you could now save around $250. Those savings don't just help pay back the initial cost of the new furnace; they also shrink your home's carbon footprint.
You can learn more about how all your system's components work together in our post on HVAC system efficiency in our comprehensive guide.
The Market Push Towards Greater Efficiency
It's not just homeowners who are chasing savings. The entire HVAC industry is being pushed toward greater efficiency, driven by rising energy costs and a growing focus on sustainability. And right at the heart of this movement are innovations in heat exchanger technology.
The demand is massive. The global heat exchanger market, which is a cornerstone of the HVAC industry, was valued at roughly USD 23 billion in 2025. It's projected to more than double, hitting USD 49.7 billion by 2035. This incredible growth is a direct response to stricter environmental regulations and higher energy prices around the world.
This market boom is fueled by the need for better heat exchangers in residential and commercial HVAC systems, where a few percentage points of efficiency can translate into huge savings and emission reductions. If you're looking to optimize your own setup, exploring professional services related to energy savings and home comfort can be a great place to start.
At the end of the day, an efficient heat exchanger in hvac units is your best defense against high energy bills, making its performance a top priority for any cost-conscious property owner.
Warning Signs of a Failing Heat Exchanger
The heat exchanger in your HVAC system works tirelessly behind the scenes, but when it starts to go, the warning signs can be subtle at first. Ignoring them is not an option. A failing heat exchanger is more than just a performance issue; it’s a serious safety hazard for your entire household.
Understanding these red flags empowers you to spot trouble early, protecting both your comfort and your family. Let's walk through the key indicators that this critical component is compromised. Knowing what to look and listen for allows you to take swift, decisive action when it matters most.
Visual Clues of a Damaged Heat Exchanger
Your first line of defense is a simple visual inspection. While a comprehensive check should always be left to a professional, you can often spot obvious signs of trouble just by looking at and around your furnace unit. Think of these physical symptoms as your furnace’s way of crying for help.
Pay close attention to these indicators:
Soot Buildup: Dark, black soot collecting on the inside surfaces of your furnace is a major red flag. This points to incomplete combustion, meaning the furnace isn't burning its fuel correctly, often due to a problem with the heat exchanger.
Visible Rust or Corrosion: The heat exchanger is made of metal that expands and contracts with every single heating cycle. Over time, exposure to moisture from combustion byproducts can cause rust and corrosion, which weakens the metal and makes it prone to cracks.
Water on the Floor: If you have a high-efficiency condensing furnace, a little water drainage is normal. However, if you notice excessive water pooling around the base of the unit, it could signal a crack in the secondary heat exchanger.
Catching these visual signs early is a key part of responsible homeownership and can prevent more serious issues from developing.
Unusual Sounds and Smells
Beyond what you can see, your senses of hearing and smell are powerful tools for detecting a failing heat exchanger in hvac systems. Furnaces make noise, of course, but any new or unusual sounds should never be ignored, as they often point directly to mechanical stress or failure.
Listen for distinct noises like rattling, popping, or banging, especially right when the furnace kicks on. These sounds can be caused by the metal of a cracked heat exchanger expanding as it heats up. The stressed metal sheets pull apart and then slap back together, creating a noise that definitely wasn't there before.
The most dangerous sign of a cracked heat exchanger is one you cannot see, smell, or taste: colorless, odorless carbon monoxide gas. Because of this silent threat, functional CO detectors are non-negotiable in any home with a fuel-burning furnace.
Similarly, be alert for strange odors. A strong smell like formaldehyde, often described as metallic or chemical-like, can be a symptom of a significant crack. This odor means dangerous combustion fumes could be leaking into the air you breathe.
The Telltale Flame and CO Detectors
One of the most definitive signs of a problem lies with the burner flame itself. A healthy furnace flame should be a steady, vibrant blue. If you peek through the observation window and see a flame that is yellow, orange, or flickering erratically, it indicates a serious combustion problem. This often means the heat exchanger is cracked and pulling in excess air, which disrupts the proper fuel-to-air mixture.
The demand for safer, more efficient units is on the rise. In the United States, the HVAC heat exchanger market was valued at approximately USD 3.8 billion in 2024 and is projected to climb to USD 5.7 billion by 2033. This growth is driven by the need for reliable systems and stricter environmental rules, pushing the industry toward more durable components.
If you observe any of these signs, the protocol is clear: shut down your furnace immediately to prevent any risk. Then, call a certified HVAC professional. Regular preventative check-ups are also crucial, which you can learn about in our essential HVAC maintenance guide. A pro can perform a definitive test to confirm if the heat exchanger is safe or needs to be replaced.
Innovations Shaping Future HVAC Systems
The trusty heat exchanger in hvac systems, a workhorse component for decades, is getting a serious upgrade. The future of heating and cooling isn’t about starting from scratch; it’s about making the core components smarter, tougher, and dramatically more efficient. We're seeing this evolution firsthand through breakthroughs in materials, intelligent monitoring, and clever new designs.
What does this mean for you? It means next-generation systems that are not only better at keeping you comfortable but are also more durable and environmentally friendly. The goal is simple: create equipment that works harder, lasts longer, and sips energy, which is a win for both your wallet and the planet.
Advancements in Materials and Design
At the heart of any great heat exchanger is the material it's built from. Researchers are now developing new metal alloys and advanced coatings that give performance a major boost. These aren’t just random metals; they are specifically engineered to transfer heat more effectively while standing up to rust and corrosion, two of the biggest reasons heat exchangers fail prematurely. That translates to a longer, more reliable service life.
Beyond the materials, the physical designs are getting a rethink, too. Technologies like microchannel heat exchangers, which use countless tiny passages to maximize the heat transfer surface area, are becoming much more common. This lets manufacturers build smaller, lighter, yet more powerful HVAC units that can meet the ever-growing demand for energy efficiency.
The core trend in modern HVAC design is clear; build systems that are smarter, tougher, and more sustainable. This shift is turning the once-simple heat exchanger into a highly engineered, data-driven component.
These design improvements deliver real, tangible benefits for homeowners. A more compact unit can be a lifesaver in tight installations, and better efficiency shows up every month on your energy bill. Of course, adopting these advanced systems can involve an upfront investment, which is why it's good to know your options. You can learn more about managing this cost by reviewing our guide on HVAC financing options and easy ways to save.
The Rise of Smart, Predictive Systems
Perhaps the biggest leap forward is the integration of smart technology. The Internet of Things (IoT) is turning the once-unassuming heat exchanger into an intelligent device that can monitor itself. By embedding tiny sensors directly into the component, these systems can track key performance metrics in real-time.
This continuous flow of data enables predictive maintenance, which is a complete game-changer for reliability. Instead of waiting for something to break on the coldest night of the year, the system can alert you or your HVAC technician to potential problems long before they lead to a total failure. This proactive approach helps you sidestep expensive emergency repairs and frustrating downtime.
This push for smarter HVAC tech is a global phenomenon. The market is growing fast, with the Asia Pacific region taking a 31.57% market share, valued at nearly USD 6 billion in 2024. This massive growth, driven by urbanization and industrialization, shows just how much demand there is worldwide for more efficient HVAC solutions. You can dig into more insights on this global trend from Precedence Research.
Ultimately, the future of the heat exchanger in hvac systems is one where intelligent data and durable design work hand-in-hand to set a new standard for comfort and efficiency.
Got Questions About Heat Exchangers? We’ve Got Answers.
As you get more familiar with how your HVAC system works, a few common questions about heat exchangers always seem to pop up. We've put together some straight-to-the-point answers to help you feel more confident about what’s happening inside your furnace.
How Long Does a Heat Exchanger Typically Last?
You can generally expect a furnace heat exchanger to last between 15 and 20 years. Think of this as a ballpark figure, not a hard-and-fast rule. The actual lifespan really comes down to the quality of the furnace, whether it gets regular professional maintenance, and even things like the humidity in your area.
The single best thing you can do to get the most years out of it is to schedule regular inspections. Putting off those routine check-ups is the quickest way to wear out this vital part and risk a much earlier failure.
Can a Cracked Heat Exchanger Be Repaired?
In almost all cases, the answer is a firm no. You might wonder if a crack could just be welded shut, but that's a dangerous and unreliable fix. The metal inside a furnace goes through extreme temperature changes, constantly expanding and contracting. A welded patch simply can’t hold up under that stress and could fail without any warning.
Because a crack poses a serious risk of carbon monoxide poisoning, the industry-wide best practice is to replace the entire heat exchanger. In many situations, given the high cost of labor for that job, replacing the whole furnace is the smarter and safer move.
What Is the Main Difference Between a Primary and a Secondary Heat Exchanger?
Every gas furnace has a primary heat exchanger; it’s the first component to grab heat from the hot gases produced by the burners. It’s the workhorse of the heating process.
High-efficiency furnaces, which usually have an AFUE rating of 90% or higher, take things a step further. They add a secondary heat exchanger to the mix. This extra stage is designed to pull even more heat from the exhaust fumes before they’re vented out. It works so well that the water vapor in the exhaust actually cools down enough to turn back into liquid water. That’s why you’ll hear these called "condensing furnaces," and it’s the secret behind their impressive energy efficiency.
For expert inspections, maintenance, or replacement of your HVAC system's heat exchanger, trust the certified technicians at Covenant Aire Solutions. We offer honest, upfront pricing and 24/7 emergency service to keep your home safe and comfortable. Contact us today at https://www.covenantairesolutions.com to schedule your appointment.
