Your Guide to the HVAC Heat Exchanger
- shawncovenantaire
- 11 minutes ago
- 13 min read
At the very heart of your furnace, there's a component working tirelessly behind the scenes to turn fuel into warmth: the HVAC heat exchanger. This isn't just some random piece of metal; it's the critical part responsible for transferring heat from the furnace's burners into the air that gets circulated through your home.
Think of it as the ultimate gatekeeper. It has the crucial job of letting the heat pass through while forming a secure barrier that keeps dangerous combustion gases safely away from your family's breathable air. This dual role, heating and protecting, makes it one of the most important components in your entire HVAC system.
What a Heat Exchanger Does for Your Home
When you break it down, the heat exchanger has one primary job with two critical functions: heat the air efficiently and keep toxic exhaust fumes safely contained.
It’s a lot like cooking soup on a gas stove. The flame heats the pot, the pot warms the soup inside, but the raw flame never actually touches your food. The heat exchanger operates on a very similar principle.
When your thermostat signals for heat, the burners in your furnace ignite. This creates intense heat along with combustion byproducts, including dangerous gases like carbon monoxide. This whole process heats up the metal walls of the heat exchanger. At the same time, your system's blower fan pushes cool indoor air across the outside of these now-hot metal walls. The air soaks up the heat, becomes warm, and is then sent through your ductwork to heat up your home. All the while, those hazardous gases stay sealed inside the heat exchanger until they're safely vented out of your house.
The Heart of Home Comfort and Safety
This separation of air streams is precisely what makes the heat exchanger so vital. Without it, your furnace couldn't generate warmth without also pumping deadly fumes directly into your living space. A properly functioning unit is what keeps your family both warm and safe when the temperatures drop.
The integrity of your heat exchanger is non-negotiable. A crack, no matter how small, can compromise the barrier between clean air and combustion exhaust, creating a serious health risk. Regular inspections are vital to catch potential issues early.
Understanding how an HVAC heat exchanger works is key to appreciating your home's overall comfort and air quality. It's especially important when you're looking at the bigger picture of smart energy-efficient home design. This single component’s performance has a direct line to your furnace’s efficiency, which is a cornerstone of a well-managed home. You can find more ways to get the most out of your system in our guide to HVAC system efficiency.
The demand for high-performance components like this is skyrocketing. The global market for heat exchangers was valued at around USD 18.9 billion and is expected to climb to USD 42.4 billion as the push for energy-saving solutions continues to grow. This massive growth just goes to show how essential these parts are to modern life.
How Your Furnace Creates and Delivers Warm Air
When your thermostat senses the temperature drop and calls for heat, it kicks off a rapid, finely-tuned sequence inside your furnace. The whole operation hinges on the hvac heat exchanger, the crucial bridge between the raw heat of combustion and the comfortable warm air that fills your home. It's a beautifully simple, yet vital, process.
The cycle starts the moment your furnace’s burners ignite, creating controlled flames and hot combustion gases. These superheated gases are funneled directly into the heat exchanger's sealed chambers, causing its metal walls to get hot fast. Often, they'll even glow a dull red.
Transferring Heat Without Mixing Air
At this point, the heat exchanger is intensely hot, but those dangerous exhaust fumes are safely contained within its walls. Next up, your HVAC system’s blower fan springs into action. It pulls cool air from your home’s return vents and pushes it across the outer surface of that hot heat exchanger.
As the cooler air rushes over the heated metal, it soaks up the thermal energy through convection. This heat transfer is incredibly efficient, quickly warming the air to the temperature you've set. Once heated, this fresh, warm air is pushed into your ductwork and circulated throughout your home, bringing the room temperature up.
This graphic breaks down that fundamental journey from combustion to comfort.
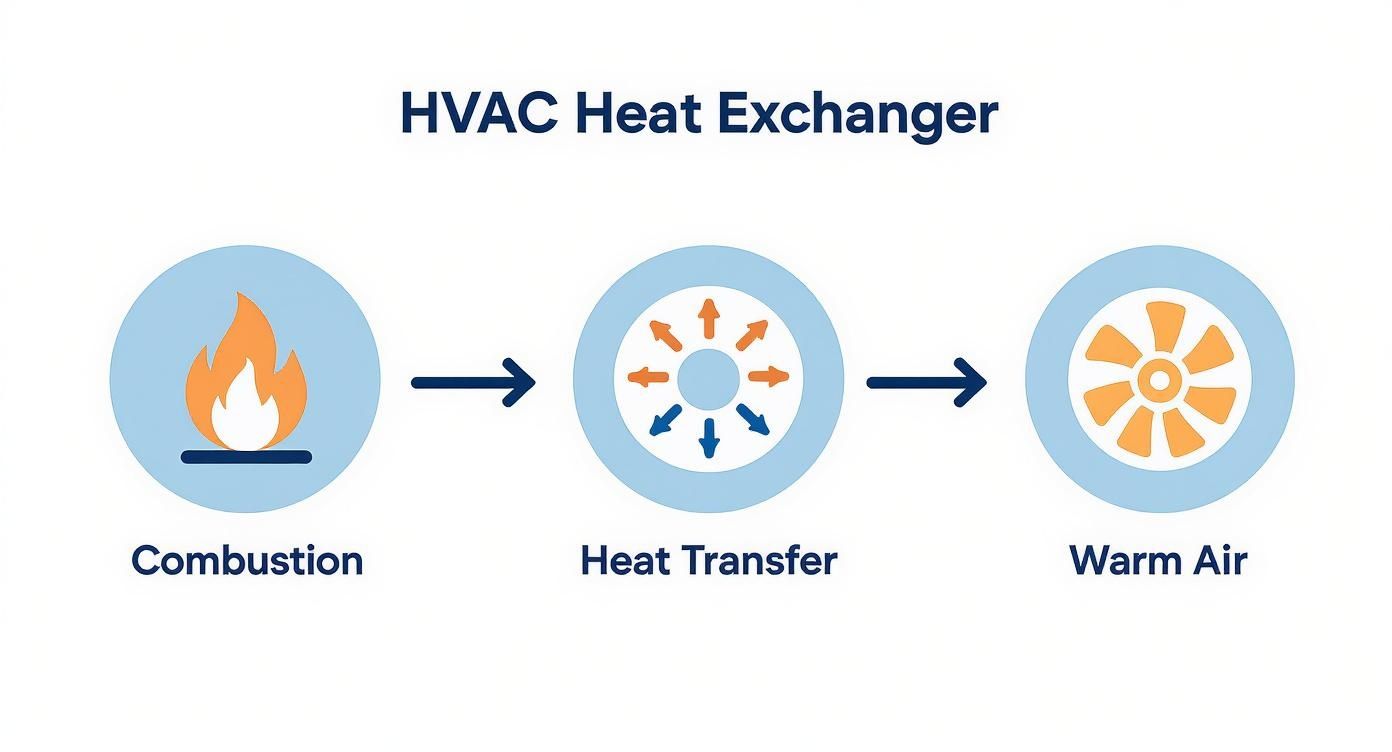
As you can see, the design keeps the combustion gases completely separate from the air you breathe, while still allowing heat to pass from one to the other.
The Final, Crucial Step
While your home is starting to feel toasty, the furnace has one last job to do. The now-cooler combustion byproducts still trapped inside the heat exchanger need to be safely vented. These gases, which include carbon monoxide, are channeled into a flue pipe that directs them completely outside your house.
This carefully engineered process guarantees two things:
Efficient Heating: Your home gets warm quickly and effectively.
Absolute Safety: The dangerous exhaust gases never mix with your indoor air.
The performance of this entire sequence is really what defines a furnace's quality and effectiveness. Different furnace technologies, for instance, handle this process with varying levels of efficiency. For anyone looking to maximize both comfort and energy savings, learning about modern options is a smart move. Our guide on what is a two-stage furnace is a great place to start, as it gives a solid overview of how newer systems refine this heating cycle.
A properly functioning heat exchanger is the unsung hero of your heating system. It’s the component that allows for the magic of turning fuel into safe, reliable warmth, ensuring your comfort during the coldest months without compromising your home's air quality.
Understanding Different Heat Exchanger Designs
Not all HVAC heat exchangers are created equal. The specific design inside your furnace directly impacts its efficiency, how long it will last, and even its price tag. While they all do the same basic job of transferring heat, the way they're built makes a world of difference.
Think of it like car engines: some are built for raw power, others for fuel economy. Heat exchanger designs are engineered with similar trade-offs in mind. In most home furnaces, you'll find one of three main types: clamshell, tubular, or condensing. Let's break down what makes each one unique.
Clamshell and Tubular Designs
The clamshell heat exchanger is one of the oldest and most common designs out there. It gets its name because it’s made from two large pieces of stamped metal that are welded together, kind of like a clam's shell. This design gives a lot of surface area for heat to transfer over, packed into a relatively small space, which makes it a go-to for many standard-efficiency furnaces.
On the other hand, the tubular heat exchanger is built from a series of individual tubes, often bent into a winding "S" shape. This design is widely considered more durable. Why? The curved construction gives the metal more room to expand and contract as it heats and cools, putting less stress on the welds. This flexibility often means a longer lifespan and a lower risk of developing cracks over time.
While both clamshell and tubular designs are effective, the choice between them often comes down to a balance of manufacturing cost and long-term durability. Tubular models typically represent a step up in resilience.
High-Efficiency Condensing Heat Exchangers
This is where modern furnace technology really shines. High-efficiency furnaces use a secondary heat exchanger, also called a condensing heat exchanger, to squeeze every last bit of warmth out of the fuel.
Here’s how it works: after the hot exhaust gases leave the primary exchanger (which is usually tubular), they aren't vented outside right away. Instead, they're sent to this second unit.
The secondary exchanger is engineered to pull so much heat from the exhaust that the water vapor in the gas actually condenses back into liquid water. This phase change releases a surprising amount of "latent heat," which is then used to help warm your home. This is the secret sauce that lets furnaces hit efficiency ratings of 90% or higher, and it's the key difference between a standard furnace and a high-efficiency one.
This push for better efficiency is a big deal. With buildings accounting for roughly 36% of global energy consumption, innovations like these are more important than ever. You can dig into some of the heat exchanger market trends to see how this demand is driving new technology forward.
Comparison of Common HVAC Heat Exchanger Types
To make things clearer, here’s a quick rundown of how these three common designs stack up against each other. Each has its place, but knowing the differences can help you understand what's working inside your own furnace.
Feature | Clamshell Heat Exchanger | Tubular Heat Exchanger | Condensing (Secondary) Heat Exchanger |
|---|---|---|---|
Primary Use | Standard-efficiency furnaces | Mid to high-efficiency furnaces | High-efficiency furnaces (90%+) |
Material | Typically aluminized or stainless steel | Often stainless steel for durability | Corrosion-resistant stainless steel or specialized alloys |
Key Advantage | Lower manufacturing cost | High durability and resistance to stress cracks | Maximizes heat extraction for ultimate efficiency |
Key Disadvantage | More susceptible to stress fractures over time | Higher initial cost compared to clamshell | Requires a drain to manage condensation |
This table helps illustrate the trade-offs between cost, durability, and raw efficiency. The right design depends entirely on the furnace's overall performance goals.
Understanding these designs gives you a much better picture of your furnace's performance. And while we've focused on heating here, the same core principles apply to cooling. Be sure to check out our guide on your air conditioner's heat exchanger to see how it all works on the other side of the thermostat.
Warning Signs of a Failing Heat Exchanger
Your furnace's heat exchanger is built tough, but it's not invincible. The constant cycle of heating up and cooling down puts a tremendous amount of stress on the metal. Over the years, this thermal stress can eventually lead to cracks or holes.
Knowing the early warning signs of a failing hvac heat exchanger is one of the most critical things you can do to protect your family. A compromised unit is a serious safety hazard, but thankfully, it usually sends out some pretty clear signals that something is wrong.

Sounds and Smells to Watch For
Often, the first clue is an unusual noise coming from your furnace area. Sure, furnaces make noise, but you need to listen for changes. Keep an ear out for rattling, popping, or banging sounds, especially right when the furnace kicks on or shuts down. These noises often mean the metal of the heat exchanger is expanding and contracting in ways it shouldn't, a classic sign of stress fractures.
Another huge red flag is any weird smell, particularly a strong, chemical-like odor similar to formaldehyde. This can happen when a crack allows combustion fumes to mix with your home's air. These aren't just minor quirks; they are direct warnings from your heating system that it needs immediate attention.
By far, the biggest danger from a cracked heat exchanger is the potential for carbon monoxide (CO) to leak into your home. This gas is odorless, colorless, and toxic. It can be fatal, which is why working CO detectors are an absolute non-negotiable in any home with a fuel-burning furnace.
Visual Clues You Can Spot
You can also be on the lookout for visual signs that point to a problem. While a professional needs to do a full inspection, you might be able to spot some of these indicators yourself.
Changes in the Burner Flame: A healthy furnace flame is steady and blue. If you see a flame that is yellow, dancing, or flickering, it could mean the heat exchanger is cracked and throwing off the proper mixture of gas and air.
Visible Soot: Finding black soot collected on the inside surfaces of your furnace is another bad sign. Soot indicates poor combustion, a common side effect of a compromised heat exchanger.
Signs of Wear and Tear: When you're doing a routine check, like changing a filter, take a quick look for any visible cracks, rust, or corrosion on the furnace components you can see. Any sign of deterioration warrants a call to an HVAC professional.
If you’re noticing issues like these or your furnace just isn't heating like it used to, you need to act fast. For more general advice, our guide on what to do when your furnace is not blowing hot air offers some great troubleshooting steps. But if you suspect a heat exchanger problem based on the signs above, professional help isn't just a good idea, it's essential.
Proactive Maintenance to Protect Your Heat Exchanger
When it comes to your furnace's heat exchanger, an ounce of prevention is truly worth a pound of cure. Taking a proactive approach to care is always less stressful and far cheaper than dealing with an emergency replacement down the road. It's the key to making sure your furnace runs safely and efficiently for its entire expected lifespan.
Getting an annual professional tune-up is the single most important thing you can do for your furnace. During these checks, a certified technician has the trained eye to spot tiny stress fractures or the beginnings of corrosion, things you'd never see on your own. Catching these problems early is what stops them from escalating into a dangerous carbon monoxide leak.

Simple DIY Tasks for a Healthy Furnace
Beyond the yearly professional visit, a few simple tasks you can do yourself will make a massive difference in protecting your heat exchanger. These easy habits directly combat the most common causes of premature failure, like overheating and poor combustion.
Change Your Air Filters Regularly: A dirty filter is the number one enemy of a healthy furnace. It chokes off the airflow, forcing the heat exchanger to get dangerously hot. This repeated stress accelerates metal fatigue and eventually leads to cracks.
Keep the Furnace Area Clear: Your furnace needs room to breathe. Piling boxes, laundry, or other clutter around the unit can easily block air intake vents, causing the same overheating issues as a clogged filter.
Ensure Vents Are Unobstructed: Make sure nothing is blocking your indoor air vents or the exterior exhaust flue. Snow drifts, fallen leaves, or even furniture pushed up against a vent can disrupt airflow and create unsafe conditions inside the furnace.
A well-maintained furnace doesn't just protect its components; it runs more efficiently, which saves you real money on your utility bills. In fact, a simple step like changing a dirty filter can improve your furnace's efficiency by up to 15%, taking a huge strain off the entire system.
These small, consistent efforts are what add up to a long-lasting and reliable heating system. If you're looking for a more detailed checklist, our guide on how to maintain your HVAC system offers a great year-round overview. A little attention now pays off big time in safety, savings, and peace of mind later on.
Navigating Heat Exchanger Replacement Costs
Getting the news that you need a new HVAC heat exchanger is one of those moments every homeowner dreads. It usually comes with immediate concerns about the final bill. The best way to tackle this is to understand what actually goes into the replacement cost, so you can make a confident decision for your home and your budget. The price you're quoted isn't just for the part itself; it's a mix of several important factors.
You can typically expect the final cost of a heat exchanger replacement to land somewhere between $1,500 and $3,500, though this can definitely swing one way or the other. The brand and model of your furnace play a huge part, as components for high-efficiency or premium furnaces naturally cost more. On top of that, labor rates in your area and the sheer complexity of the job will also have a big impact on the total price.
Key Factors That Shape the Price
A few key variables will determine what that final invoice looks like. Knowing what they are before you get a quote helps you understand exactly what you're paying for.
Part Cost: The heat exchanger itself can run anywhere from $500 to over $1,500. It all depends on your furnace's make and its efficiency level.
Labor Hours: This is not a quick swap. A replacement is a labor-intensive job that often takes a skilled technician four to eight hours to carefully take the furnace apart, install the new component, and put everything back together correctly.
Warranty Coverage: Here’s some potentially good news. If your furnace is still under its manufacturer's warranty, the part itself might be covered. You will, however, almost always be responsible for the labor costs.
This whole repair and replacement cycle is part of a massive industry. In fact, the United States heat exchanger market has hit USD 3.8 billion and keeps growing, fueled by the demand for more energy-efficient and dependable HVAC solutions. You can read more about the growth of the heat exchanger market at IMARC Group.
The Big Question: Repair or Replace the Furnace?
When you're facing a major repair bill on an older furnace, it always brings up a critical question: Does it make more sense to fix this one part, or should I put that money toward a completely new system? The right answer really hinges on the age and overall condition of your current furnace.
As a general rule of thumb, if the repair cost is approaching 50% of what a new furnace would cost, and your current unit is over 10-15 years old, replacement is usually the smarter financial move in the long run.
Putting your money into a new furnace gets you a lot more than just a new heat exchanger. You get the benefit of a brand-new warranty on all the components, a major boost in energy efficiency that will lower your monthly utility bills, and the simple peace of mind that comes with modern, reliable heating technology. While the upfront cost is higher, the long-term savings and reliability often make it the wiser path.
Common Questions About Heat Exchangers
Even after you get the basics down, it’s natural to have a few more specific questions about your furnace’s heat exchanger. Getting straight answers is the key to understanding why taking care of this component is so important.
What Causes a Heat Exchanger to Crack?
The number one culprit behind a cracked heat exchanger is simply metal fatigue. Think about it: your furnace clicks on and off thousands of times each winter. Every single time, the metal of the heat exchanger expands with the heat and then shrinks as it cools down.
Over many years, this constant flexing creates stress, which can eventually lead to tiny cracks. Things like a clogged air filter can make it even worse by causing the furnace to overheat, which puts the metal under extreme strain and speeds up the failure process significantly.
Why Must a Cracked Unit Be Replaced Instead of Repaired?
Safety. It’s that simple. Trying to weld or patch a crack in a heat exchanger is never a safe or permanent solution. It might seem like a quick fix, but the intense temperature swings inside the furnace would cause that repair to fail almost immediately.
Once that happens, the pathway for deadly carbon monoxide to seep into your home is wide open again.
Because the risk of a carbon monoxide leak is so incredibly high, industry safety standards and all manufacturer guidelines strictly prohibit any attempt to repair a cracked heat exchanger. The only safe and responsible choice is a full replacement to protect your family.
What Is the Lifespan of a Heat Exchanger?
A well-maintained heat exchanger should last as long as the furnace itself, which is typically in the ballpark of 15 to 20 years. But getting it to last that long isn't a given; it really depends on a few critical factors:
Regular Maintenance: Getting a pro to look at it once a year is the best way to catch small problems before they become big ones.
Proper Airflow: This is a big one. Just changing your air filters on schedule prevents the furnace from overheating and putting extra stress on its parts.
Correct Installation: If the furnace was the wrong size for your house or wasn't installed correctly from the get-go, it could have been straining the heat exchanger from day one.
In the end, consistent professional care is what will help your heat exchanger live out its full, safe lifespan.
If you're worried about your furnace or think there might be an issue with your hvac heat exchanger, don't put it off. Contact the certified professionals at Covenant Aire Solutions for a thorough inspection and honest advice. Visit us at https://www.covenantairesolutions.com to schedule your service today.

