What Is a Heat exchanger? Learn How It Works and Types
- shawncovenantaire
- Aug 21, 2025
- 13 min read
Ever wonder how your car engine stays cool or your refrigerator keeps your groceries from spoiling? The answer is often a device working silently behind the scenes: a heat exchanger.
Think of it as a bridge for heat. It's designed to let thermal energy move from a hot fluid to a cold fluid without the two ever actually mixing.
The Unseen Engine of Thermal Transfer

At its heart, a heat exchanger is the technology that makes countless modern conveniences possible, from home heating to industrial power generation. It’s an engineered system specifically designed to efficiently transfer, or exchange, heat between two or more fluids.
It’s a process we see in everyday life. Imagine stirring hot coffee with a cold metal spoon. The spoon gets warm, right? That's a simple example of heat transfer. A heat exchanger just takes that basic principle and refines it, creating a controlled environment where this energy exchange is maximized for a specific job.
Mastering Thermal Management
The primary goal here is to manage thermal energy with precision. Instead of just letting heat dissipate randomly, these devices direct it exactly where it's needed or pull it away from where it’s not.
This is all done without any direct contact between the substances involved. A solid barrier, usually made of a metal with high thermal conductivity like steel or copper, separates the two fluids. This wall allows heat to pass through easily while preventing any cross-contamination.
A heat exchanger is a master of thermal efficiency. It harnesses the natural tendency of heat to move from warmer to cooler areas, making our machines and systems more effective, safer, and more energy-conscious.
This simple yet powerful concept is behind so much of our technology. Understanding what a heat exchanger is really sets the stage for appreciating its diverse roles, especially within your home's comfort systems. To dive deeper into its most common application, you can explore the critical role of the heat exchanger in HVAC explained in our detailed guide.
The core functions of a heat exchanger can be broken down into a few key objectives:
Heating: Transferring heat from a hot source to a colder fluid, like how a furnace warms the air that circulates through your home.
Cooling: Removing heat from a substance to make it colder, which is exactly what your air conditioner does to cool indoor air.
Energy Recovery: Capturing waste heat from an industrial process so it can be reused, which boosts overall efficiency and saves money.
To really get a handle on what a heat exchanger does, it helps to first understand how heat behaves on its own. Think of thermal energy as something that's always on the move, naturally flowing from a warmer spot to a cooler one until everything evens out. Heat exchangers are simply clever devices designed to take control of this natural flow.
They work by mastering the three fundamental ways heat gets from point A to point B.
The first and most straightforward method is conduction. This is when heat travels right through a solid object, or between two things that are physically touching.
Ever leave a metal spoon in a hot cup of coffee? In no time, the handle gets warm, even though it never touched the liquid. Heat literally walked its way up the solid spoon, molecule by molecule. That’s conduction in a nutshell.
The Power of Flowing Currents
Next up is convection. This is what happens when heat is carried along by the movement of a fluid, and in this world, "fluid" just means a liquid like water or a gas like air.
A perfect example is a pot of water boiling on the stove. The burner heats the very bottom of the pot through conduction. As that water gets hot, it becomes less dense and starts to rise. At the same time, the cooler, denser water from the top sinks to take its place, gets heated, and rises too.
This constant circulation is called a convection current, and it's an incredibly efficient way to spread heat through the entire pot. Heat exchangers often create these controlled currents to shuttle thermal energy from one place to another, fast.
This is the exact same principle your furnace uses. It heats up air (the fluid), which then circulates through your home's ductwork to deliver warmth to every room.
The Invisible Transfer of Heat
Finally, we have radiation. This is the wild one, because it doesn't need any direct contact or even a medium like air or water to travel through. Heat moves as invisible electromagnetic waves, just like light.
You feel this every single day when the sun warms your skin from 93 million miles away. You also feel it when you stand near a bonfire; that warmth hitting your face is mostly thermal radiation. While conduction and convection do most of the heavy lifting inside a typical heat exchanger, radiation always plays a part in the total energy transfer.
Once you understand these three mechanisms, it’s easy to see how engineers can design a heat exchanger to be so effective. They’re not fighting against the laws of physics; they’re using them on purpose to move heat exactly where it’s needed, making our homes comfortable and our industries run smoothly.
Comparing the Most Common Heat Exchanger Designs
Not all heat exchangers are created equal; different jobs demand different tools. While the ultimate goal of transferring thermal energy is always the same, the actual design changes dramatically based on the specific job, the fluids involved, and the pressures and temperatures it has to handle.
Getting a feel for these designs is the best way to understand what a heat exchanger is in a practical sense. Let's break down three of the most common types you'll run into, from massive industrial plants to the HVAC equipment in your own home.
This visual gives you a great at-a-glance look at these key models and where they fit in the world of thermal management.
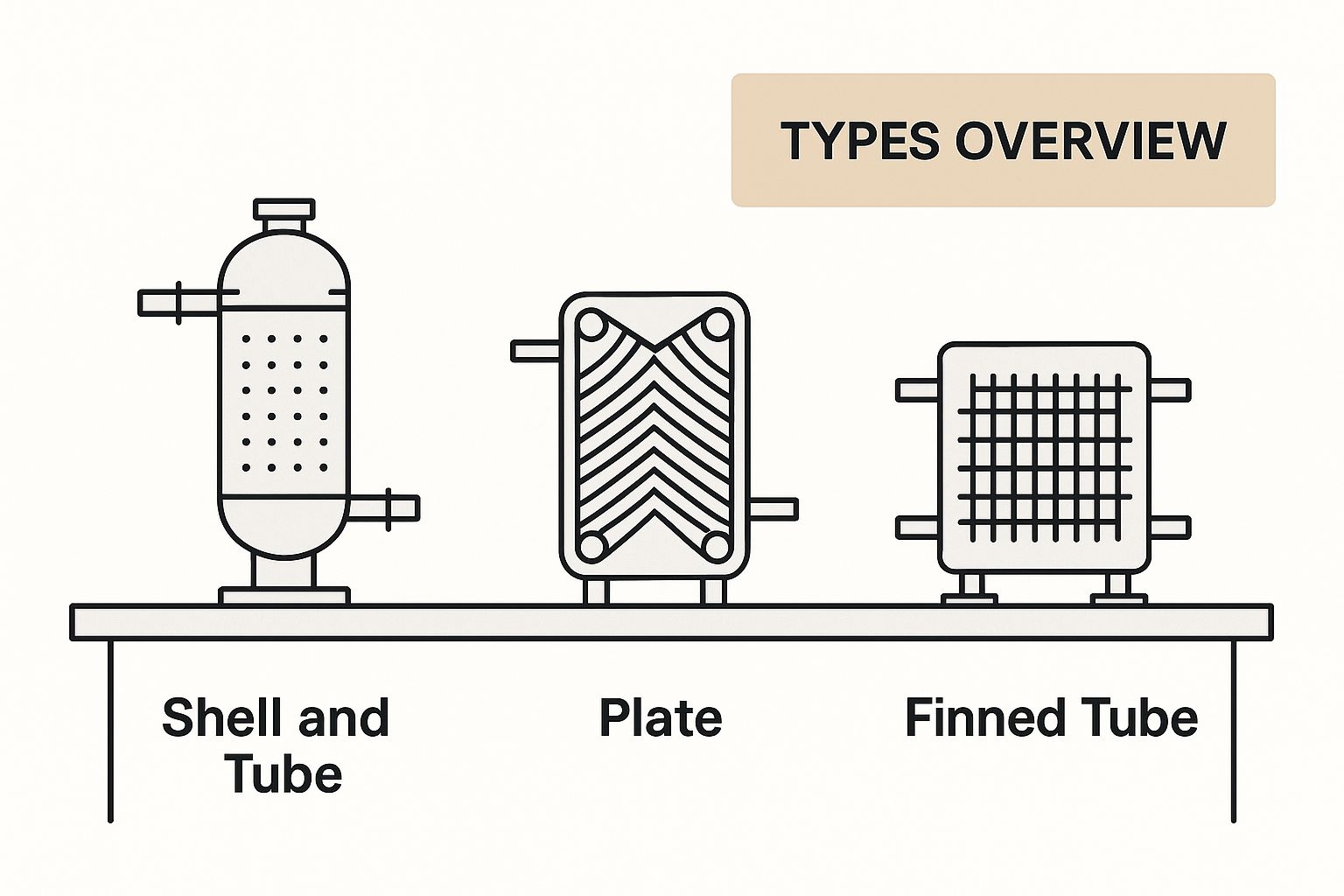
You can see how the designs range from robust, large-scale workhorses to more compact, intricate models, really showing how form follows function.
Shell and Tube Exchangers
The shell and tube heat exchanger is the undisputed workhorse of the industrial world. It's famous for its sheer durability and ability to handle incredibly high pressures and temperatures.
Picture a large cylinder (the shell) packed with a bundle of smaller pipes (the tubes). One fluid flows through all the little pipes, while the second fluid fills the bigger cylinder, flowing over and around the tube bundle to make the heat transfer happen.
This design is incredibly robust, making it the go-to choice for demanding places like oil refineries and large-scale chemical processing plants. While it’s tough, it's often bulky and not as thermally efficient for its size compared to more modern designs.
Plate and Frame Exchangers
For a more compact and often more efficient alternative, look no further than the plate and frame heat exchanger. Imagine a neat stack of thin metal plates, each one pressed with a corrugated pattern like a piece of cardboard. These are stacked together with gaskets sealing the edges, creating a series of alternating channels for the hot and cold fluids.
The liquids flow in thin layers on opposite sides of each plate, which creates a massive surface area for heat transfer in a very small footprint. This makes them highly efficient and perfect for liquid-to-liquid jobs where space is tight, like in modern HVAC systems or food and beverage production.
The key takeaway here is the trade-off. Shell and tube models offer ruggedness for extreme conditions, while plate and frame exchangers deliver superior thermal efficiency in a much smaller package.
Their main limitation is that the gaskets can be a weak point, making them less suited for the extreme pressures a shell and tube design can handle. In fact, some industry data shows that 72% of certain heat exchanger failures were linked to improper fluid quality, which really drives home how important it is to match the right design to the right operating conditions.
Air-Cooled Exchangers
Finally, we have the air-cooled heat exchanger, which is probably the one you're most familiar with, even if you don't recognize the name. Your car's radiator is a classic example.
In this design, a hot fluid flows through a series of tubes that are covered in thin metal "fins." A fan then blows ambient air across these fins. The fins are there to drastically increase the surface area exposed to the air, allowing heat to escape quickly from the fluid and dissipate into the atmosphere.
These are essential when a liquid cooling source like water isn't available or practical. You’ll find them everywhere, from power plants and industrial air compressors to all sorts of mobile machinery.
Each of these designs masterfully applies the same fundamental principles of heat transfer, but each one is tailored perfectly for the job it needs to do.
To help you keep these straight, here’s a quick side-by-side look at how these common types stack up against one another.
Comparing Common Heat Exchanger Types
Heat Exchanger Type | Primary Design | Typical Efficiency | Common Applications | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Shell and Tube | A bundle of tubes is housed within a larger cylindrical shell. Two fluids exchange heat without mixing. | Moderate | Oil refineries, power plants, chemical processing | High durability; handles extreme pressures and temperatures. |
Plate and Frame | A series of stacked, corrugated plates create alternating channels for hot and cold fluids. | High | HVAC, food and beverage, refrigeration | Compact size and superior thermal efficiency. |
Air-Cooled | A hot fluid flows through finned tubes while a fan blows ambient air across them to dissipate heat. | Lower | Car radiators, industrial compressors, mobile machinery | Simple, reliable, and doesn't require a liquid coolant source. |
Understanding these core differences makes it much easier to see why one design is chosen over another for a specific application. It's all about balancing performance, durability, and cost for the task at hand.
The Role of Heat Exchangers in Everyday HVAC
Heat exchangers are the unsung heroes of your home's comfort system, working silently behind the scenes to keep you warm in the winter and cool in the summer. They are the critical bridge connecting the science of heat transfer to your daily life, operating right at the heart of your furnace and air conditioner.
Think of the furnace tucked away in your basement or closet. When it fires up, it burns fuel like natural gas to create intense heat. The heat exchanger is the component that safely captures this thermal energy, transferring it to the air that circulates through your home, all without ever letting dangerous combustion fumes like carbon monoxide mix with the air you breathe.
Keeping You Warm and Safe
A furnace heat exchanger is usually a set of metal tubes or clamshell-shaped chambers. The hot exhaust gases from the combustion process flow through the inside of these chambers, heating the metal walls to a very high temperature.
At the same time, your system’s blower fan pushes cool household air over the outside of these hot chambers. As the air passes over, it soaks up the heat through convection and is then sent throughout your house via the ductwork, wrapping you in comfortable warmth. This whole process is designed for safety and efficiency, with the heat exchanger acting as a crucial barrier.
The primary job of a furnace heat exchanger is twofold: it must efficiently transfer heat while also completely isolating toxic flue gases from the air you breathe. A failure in this component is a serious safety concern.
Cooling Your Home in the Summer
The process essentially flips when you switch on your air conditioner. Here, the heat exchanger, often called an evaporator coil in this context, works to pull heat out of your indoor air.
Warm, humid air from your home is blown across the cold evaporator coil, and the heat is absorbed by the refrigerant flowing within. This chills the air, which is then sent back into your living spaces. Understanding how these components work in different systems is key; you can learn more in our guide to residential HVAC system types. For a deeper dive into how these devices fit into larger building designs, you can explore the intricacies of MEP engineering principles applied in modern construction.
The HVAC world is closely tied to construction, increasingly using heat exchangers to manage temperatures in all kinds of buildings. The efficiency of this single component directly impacts your energy bills and overall comfort, making it a critical piece of modern living.
Powering Industries From Refineries to Food Production

While heat exchangers are quietly keeping our homes comfortable, their true power is unleashed on an industrial scale. These devices are the unsung workhorses of the global economy, driving massive processes that power our daily lives: from generating the electricity we use to producing the food we eat.
Think about a power plant. The enormous heat exchangers inside are responsible for boiling water into high-pressure steam, the very force that spins massive turbines to generate electricity. In oil and gas refineries, they are just as critical. They meticulously control temperatures to separate crude oil into gasoline, diesel, and other valuable products we rely on every day.
The Backbone of Manufacturing and Production
The role of a heat exchanger doesn't stop with heavy industry. In chemical processing plants, they provide the precise temperature control needed to ensure reactions happen safely and efficiently. Without them, making everything from plastics to life-saving pharmaceuticals would be next to impossible.
This technology is also a cornerstone of the food and beverage world. Take milk pasteurization, for instance. That process involves heating milk to a specific temperature to kill harmful bacteria and then cooling it down just as quickly. This entire cycle is managed by plate heat exchangers, guaranteeing our food is safe without sacrificing quality. Even specialized tasks like achieving perfect ice cream refrigeration depend on these devices to maintain exact product standards.
From the fuel in your car to the milk in your fridge, industrial heat exchangers are the unseen technology making it all possible. Their efficiency directly impacts production costs, energy consumption, and environmental sustainability on a global scale.
You can't overstate the economic importance of this technology. The global heat exchanger market is a massive, growing industry, valued at around USD 18.9 billion in 2024 and projected to climb to roughly USD 32.96 billion by 2033. This surge is fueled by relentless demand across key sectors where managing heat is everything.
Innovations Driving Efficiency and Sustainability
Constant innovation in heat exchanger design is unlocking huge gains in industrial efficiency. Even a tiny improvement can translate into millions of dollars in energy savings for a large facility and lead to a significant drop in carbon emissions.
As industries face growing pressure to operate more sustainably, the humble heat exchanger remains one of the most powerful tools for hitting those environmental goals. Of course, the design is only half the battle; proper maintenance is essential. In an HVAC context, for example, simple upkeep makes a world of difference. You can see what we mean in our guide on how to clean an AC condensate drain line like a pro.
Essential Maintenance and Safety Checks
To keep a heat exchanger running smoothly and safely, you can't just set it and forget it. Proactive maintenance is absolutely non-negotiable. Think of it like your car's engine; it needs regular oil changes to work right. This critical component needs the same consistent attention to head off expensive failures and make sure it performs as it should. If you let it go, you're looking at lower efficiency, higher energy bills, and even serious safety risks.
The most common enemy of performance is something called fouling. It’s just a technical term for the buildup of gunk, like scale, rust, or sediment, on the heat transfer surfaces. This layer of grime acts like an insulator, forcing your system to work way harder to get the same heating or cooling result. The only way to fight this slow creep of inefficiency is with regular cleaning.
Preventing Buildup and Corrosion
Your first line of defense is simply keeping an eye on things. Regular inspections can help you catch small issues, like a minor leak or the first signs of corrosion, before they blow up into a catastrophic failure.
A few key tasks are crucial for proper upkeep:
Routine Cleaning: Getting rid of any scale, sludge, or biological growth is the best way to restore the heat exchanger’s performance and prevent clogs.
Corrosion Checks: A simple visual inspection for rust or wear, especially where components connect, is vital for a long service life.
Ensuring Proper Flow: You need to verify that fluids are moving at their designed rates. This prevents overheating and pressure buildup that can put a huge strain on the equipment.
The single most dangerous failure in a residential furnace is a cracked heat exchanger. This physical breach allows deadly, odorless carbon monoxide gas to mix with the clean air circulating in your home, creating a life-threatening situation.
This is exactly why professional inspections aren't just a good idea; they're essential for your family’s safety. Technicians have specialized tools that can spot microscopic cracks completely invisible to the naked eye. Annual checks are an absolute must.
For any homeowner, sticking to a consistent maintenance schedule is the best way to protect both your equipment and your peace of mind. To get a clear idea of what that looks like, check out our guide on creating your essential HVAC maintenance schedule to help you stay on track.
Frequently Asked Questions About Heat Exchangers
As we’ve unpacked what a heat exchanger is, some practical questions always come up. Let’s tackle some of the most common ones to clear up any lingering confusion, especially when it comes to safety and performance in your home’s HVAC system.
Getting these answers straight is crucial for any homeowner.
How Do I Know If My Furnace Heat Exchanger Is Cracked?
A cracked heat exchanger is a serious safety risk, so knowing the warning signs is non-negotiable. You might notice strange smells when the furnace kicks on, see soot building up around the unit, or spot a flickering, yellow flame where a steady blue one should be.
Even physical symptoms like frequent headaches could be a red flag for a carbon monoxide leak. The scary part is that many cracks are completely invisible to the naked eye.
The only way to know for sure is to have a professional inspect it. And please, always have working carbon monoxide detectors installed on every level of your home. They are an absolutely essential layer of protection against this silent danger.
Can a Heat Exchanger Be Repaired?
For a residential furnace, the answer is almost always a hard no. Repairing a cracked heat exchanger isn’t just a bad idea; it’s often prohibited by manufacturers and local safety codes. The metal is under constant stress from intense heat and pressure changes, which makes any weld totally unreliable. It's just too big of a risk for carbon monoxide to leak into your home.
In just about every case, the entire component or the furnace itself has to be replaced to guarantee safe operation. While some massive industrial units might be repairable by specialists, that’s not a safe bet for the equipment in your home. The cost of a new system can be a concern, but there are often ways to manage it; our guide on HVAC financing options can help you explore different ways to save.
What Is the Most Efficient Type of Heat Exchanger?
For liquid-to-liquid jobs, the plate and frame heat exchangers are generally the efficiency champions. Their clever design packs a massive amount of surface area into a really compact space, which makes for incredibly effective heat transfer.
But "most efficient" always depends on the specific task. You can't just pick one and call it a day. You have to consider things like:
The pressure and temperature of the fluids involved.
Whether the fluids are corrosive.
The risk of clogging or fouling from impurities.
Ultimately, the right choice is always a balance between raw thermal performance and the rugged durability needed for the job at hand.
When it comes to making sure your home's heat exchanger is safe and running efficiently, you really need a professional's eye. Covenant Aire Solutions offers comprehensive inspections, maintenance, and replacement services to keep your HVAC system running perfectly. Contact us today and get some peace of mind.
